Choosing the Right Communication Protocol for Industrial IoT
LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, or DigiMesh?
Key Takeaways for Industrial IoT Leaders
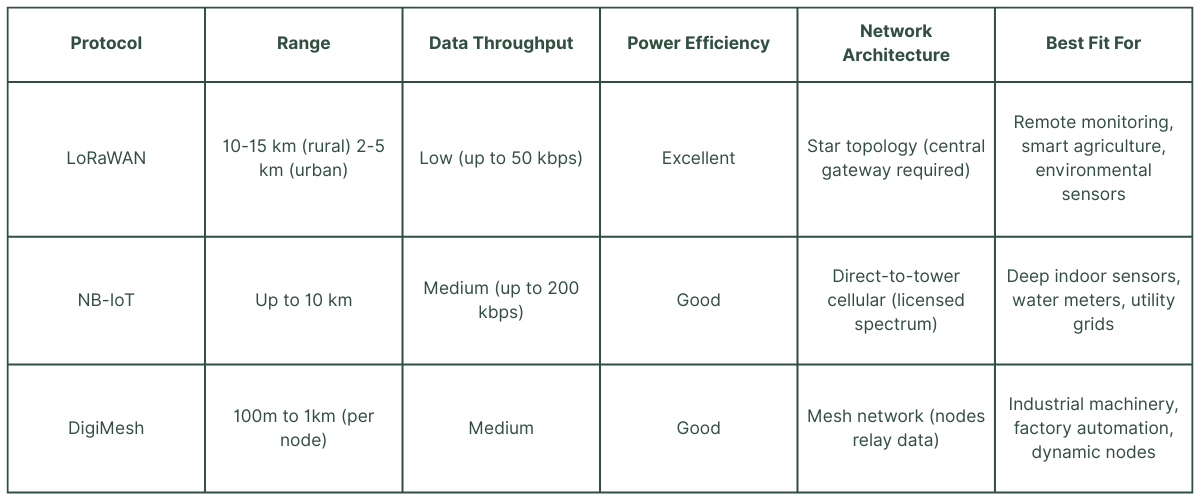
LoRaWAN offers excellent long-range communication with low power consumption but is best suited for small, infrequent data packets.
NB-IoT excels in cellular coverage and deep indoor penetration, ideal for remote deployments requiring larger data transfers.
DigiMesh stands out for its robust mesh network topology, making it ideal for dynamic industrial environments with multiple nodes requiring constant connectivity.
The best protocol depends heavily on your data size, communication frequency, and environmental constraints. For facility and operations leaders tasked with deploying sensors, gateways, and monitoring solutions, understanding which protocol aligns with your needs can make the difference between seamless data collection and costly downtime.
Understanding the Key Differences
While all three protocols facilitate low-power, wide-area communication for IoT devices, their distinct characteristics define their ideal use cases. Here's a breakdown of their strengths and limitations:
Range vs. Data Throughput: Choosing the Right Fit
While LoRaWAN provides the greatest range, this comes at the cost of data throughput. NB-IoT strikes a balance by using existing cellular networks to extend range while offering faster data rates. DigiMesh, on the other hand, sacrifices range for exceptional network flexibility. To simplify the trade-offs:
For small, infrequent data packets over long distances: LoRaWAN is the ideal choice.
For consistent data reporting from hard-to-reach locations: NB-IoT excels in providing cellular-grade coverage even underground or inside thick-walled facilities.
For localized environments requiring constant connectivity across many nodes: DigiMesh offers unmatched network resilience, with each device acting as both transmitter and receiver.
Data Size Considerations
When choosing a protocol, data packet size is critical. Here's how the three technologies compare:
LoRaWAN: Designed for small payloads (up to 243 bytes per packet). Transmitting larger data sets can cause delays, making it unsuitable for real-time applications.
NB-IoT: Supports packet sizes up to 1600 bytes, enabling frequent status updates or bulk data transfers.
DigiMesh: Flexible packet size and node-to-node communication ensure effective data exchange in localized settings. However, scaling the number of nodes may require tuning for optimal performance.
Application-Specific Recommendations
Selecting the right protocol isn't just about technical specs; it's about aligning with your operational priorities. Here are some actionable insights based on common IIoT applications:
LoRaWAN
Remote Environmental Monitoring. Its long range and low power consumption are ideal for sensors monitoring air quality, soil moisture, or temperature in remote locations.
Pipeline and Tank Level Monitoring. LoRaWAN’s low power draw extends battery life, minimizing maintenance requirements in remote oil and gas applications.
NB IoT
Smart Utility Metering. NB-IoT's ability to penetrate walls and function in dense urban settings makes it ideal for metering applications requiring consistent data transmission.
Cold Chain Monitoring in Warehouses. Its ability to reliably penetrate dense building materials ensures real-time temperature data reaches central systems.
DigiMesh
Factory Automation and Machinery Monitoring. DigiMesh’s self-healing network is perfect for managing dozens of industrial devices that require constant connectivity in changing layouts.
Mining and Tunneling Operations. Both protocols excel in challenging environments, with NB-IoT providing direct-to-tower connectivity and DigiMesh offering flexible node positioning underground.
Frequency Considerations by Region
United States: LoRaWAN operates in the 902-928 MHz ISM band, while NB-IoT leverages standard LTE frequencies. DigiMesh typically uses 2.4 GHz for consistent global compatibility.
European Union: LoRaWAN operates in the 863-870 MHz band, aligning with EU frequency guidelines. NB-IoT follows LTE spectrum standards. DigiMesh’s 2.4 GHz frequency remains consistent.
Middle East: Frequencies vary by country. Some nations follow EU standards, while others align with US frequencies. LoRaWAN deployments require local frequency checks.
Asia: Regulations are more fragmented. LoRaWAN commonly uses the 920-925 MHz band in China and the 923-925 MHz band in Southeast Asia. DigiMesh's 2.4 GHz frequency ensures seamless integration across regions.
Safety Considerations for Radiating Devices
When deploying LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, or DigiMesh devices, organizations must prioritize safety measures to minimize interference risks and comply with local regulations. Implementing these safety protocols will safeguard equipment performance, data integrity, and compliance with industry standards.
Install Devices Away from Critical Equipment. Position IoT nodes to prevent signal interference with nearby machinery or communication systems.
Follow Power Output Regulations. Each region imposes limits on transmission power to minimize health risks and ensure network harmony.
Ensure Proper Grounding. Devices with external antennas should be grounded to reduce the risk of electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Training and Awareness. Ensure deployment teams are trained in safe handling and installation practices to mitigate risks related to electromagnetic radiation.
Maximizing Battery Life in IIoT Deployments
In IIoT deployments where devices are designed to operate for years on battery power, selecting the right communication protocol is only part of the equation. Additional strategies for maximizing battery performance include:
Adaptive Reporting Intervals: Sensors that reduce their reporting frequency during stable conditions conserve significant energy.
Event-Triggered Alerts: Devices that transmit data only upon detecting anomalies dramatically improve power efficiency.
Optimized Power Profiles: Ensuring devices switch to low-power sleep modes during idle periods extends battery life without compromising performance.
Incorporating these strategies alongside the appropriate protocol selection can extend device life, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall network reliability.
Final Recommendations for Industrial IoT Leaders
When choosing a protocol, consider:
Deployment Environment: Remote locations, dense urban zones, or dynamic industrial settings will each require different strengths.
Power Constraints: Devices running on battery power may lean heavily on LoRaWAN for efficiency.
Data Size and Frequency: Bulk data or frequent updates are best served by NB-IoT or DigiMesh.
The right communication protocol can significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of your IIoT deployment. By aligning your data needs, operational conditions, and scalability requirements with the appropriate technology, you can ensure robust performance and a faster return on investment.
For tailored recommendations or strategic guidance in implementing IIoT solutions, reach out to Pêche Strategy. Our expertise can help you make informed decisions that align with your business goals.